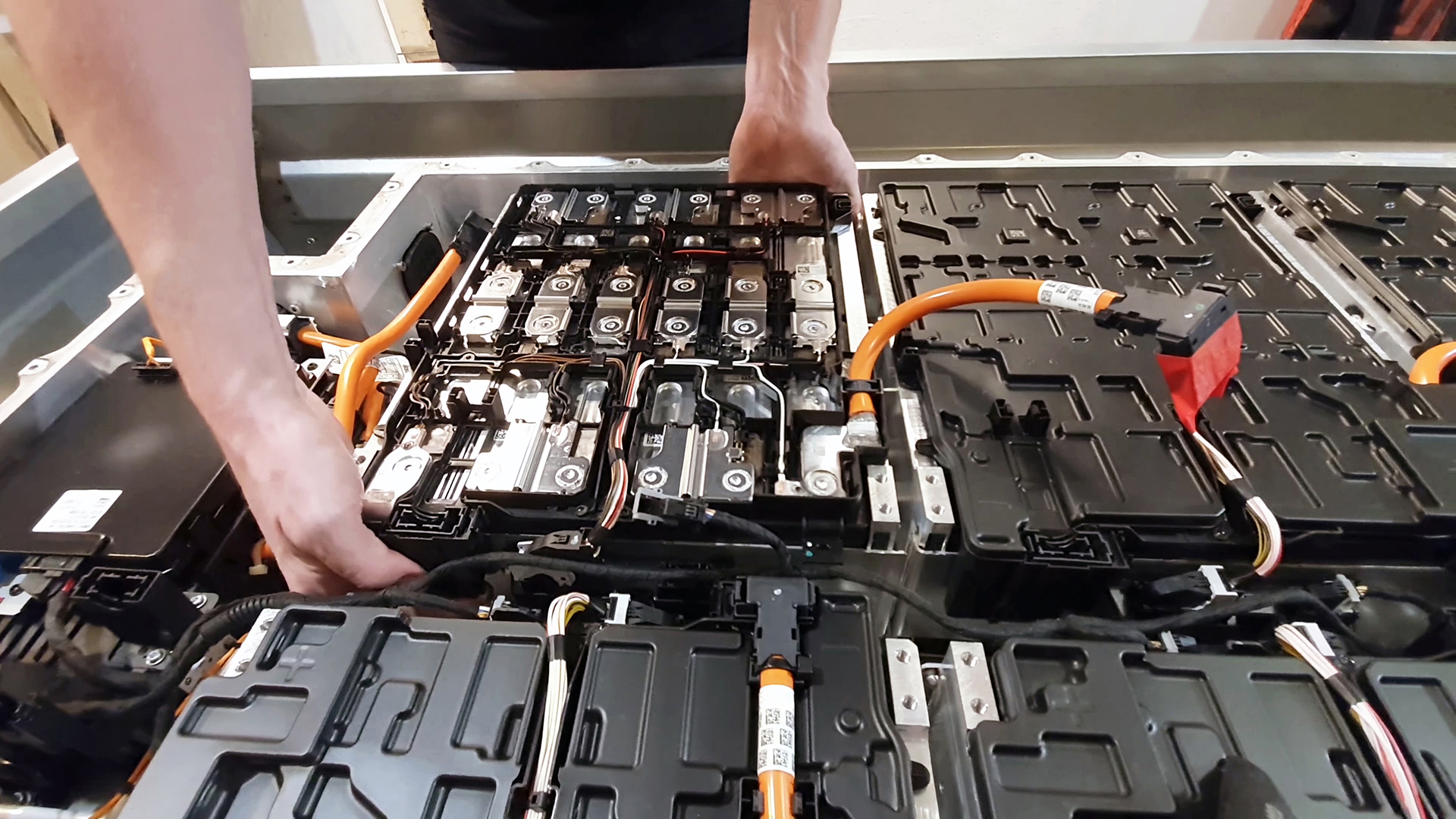
The Recycling Renaissance: Transforming Trash into Treasure
The electric vehicle and energy storage revolution brings a vital question: what to do with all the used batteries? We are amidst a "recycling renaissance," turning waste into treasure.
Leaders Paving the Way
Key players are innovating in battery recycling through "closed-loop" systems, using reclaimed materials to manufacture new batteries. This approach significantly reduces waste and extraction of new raw materials.
For instance, a leading company processes over 130,000 tons of batteries annually, recovering lithium, nickel, and cobalt. This recovery not only supports sustainability but also makes economic sense. Partnerships between international companies enhance these initiatives, underlining the importance of collaboration.
Sodium-ion technology is also gaining attention, providing safer alternatives to traditional materials. This trend helps reduce dependence on scarce resources and introduces efficiency across the industry.
Market Expansion and Global Development
The battery industry is expanding rapidly due to increased electric vehicle adoption. Notably, North America has emerged as a significant hub for both battery production and recycling, reducing transportation costs and environmental impact.
Innovations span from sodium-ion to advanced recycling of lead-acid batteries, alongside partnerships that transform waste into valuable resources in the battery sector. This synergy between technology and partnership accelerates the path toward a sustainable future.
Innovation in Lithium Recovery
Investments are reshaping lithium recovery processes and battery supply chains, focusing on reducing waste and increasing efficiency.
Technological Advancements
New processes like a zero-waste lithium hydroxide system revolutionize the traditional extraction and recycling methods. These developments minimize water usage and waste while maintaining high recovery efficiency.
Such eco-friendly innovations demonstrate the potential to source lithium sustainably for evolving industries, like electric vehicles. The seamless conversion of battery waste into valuable materials symbolizes profound progress toward a circular economy.
Collaboration between industries fosters these advancements, demonstrating the crucial alignment of public policies and private innovation towards greener practices.
Bridging Gaps: Demand and Recycling Capacity
Despite rising battery demand, recycling capabilities are lagging, creating a noticeable recycling gap.
Challenges of Increasing Demand
Electric vehicle adoption and renewable energy expansion increase demand for efficient battery storage. This demand places stress on supply chains for critical raw materials like lithium.
Raw material scarcity and fluctuating prices further complicate planning for manufacturers. Securing supply chains and exploring alternative chemistries become necessary strategies to ensure continuity.
Addressing Recycling Shortfalls
The gap between battery production and recycling capacity poses substantial challenges. Current recycling facilities struggle to manage the volume of spent batteries, risking loss of valuable resources.
Developing robust recycling infrastructures is vital. Closed-loop systems can alleviate this issue by ensuring materials are reclaimed and reused efficiently. Companies investing in such advancements are setting a standard for future sustainable practices.
Shaping Tomorrow: Trends Redefining Recovery Strategies
The dynamic landscape of battery recycling requires adaptive strategies influenced by current market trends.
Rise of Closed-Loop Systems
Closed-loop systems represent innovation, capturing and reusing almost all components of old batteries to produce new ones. Companies like CATL exemplify this approach, ingeniously sourcing materials from existing batteries to mitigate environmental and economic impacts.
Strategic Collaborations
Strategic partnerships have become integral as companies seek synergies with specialized recyclers. These collaborations allow corporations to recover resources efficiently, without the need for extensive infrastructure-building investments.
For instance, LG Energy Solution's partnership with Li-Cycle empowers sustainable operations, illustrating how collective expertise can meet ambitious sustainability targets.
Embracing Domestic Solutions
There is a push to localize battery manufacturing and recycling, motivated by factors such as supply chain resilience, environmental conservation, and economic growth. Domestic recycling hubs help recover and utilize materials within borders, reducing dependency on foreign entities.
Such initiatives support the creation of jobs and technological advancements, steering the industry towards a sustainable and economically viable future.
Building a Greener Future: Collaborative Roles of Sectors
The alliance between public and private sectors is crucial in advancing battery recycling as a cornerstone of a greener future.
Governmental and Business Synergy
Governments establish the framework for recycling initiatives, providing incentives and enforcing policies that motivate corporations to invest in cutting-edge technologies and infrastructure.
Businesses drive innovation by developing processes to reclaim essential metals for new batteries. Their investments in research and partnerships enhance overall recycling capabilities.
Circular Economy Integration
The vision is to embed a circular economy, ensuring that old batteries are not merely discarded but broken down and reimagined as new resources. This system encourages efficiency and sustainability, emphasizing the responsible lifecycle of battery materials.
The journey involves overcoming challenges like high recycling costs, standardizing processes, and logistics improvements. Progress will lead us closer to a world where resources are consistently optimized, embodying the essence of sustainability.
Question and Answer
-
What are the current innovations in lithium recovery, and how do they contribute to sustainability?
Innovations in lithium recovery have significantly advanced, focusing on eco-friendly processes that minimize environmental impact. For instance, a zero-waste lithium hydroxide production process developed in Germany reduces water usage and waste discharge, maintaining high efficiency. These innovations contribute to sustainability by ensuring that lithium, a critical component in batteries, is sourced responsibly, thus supporting the circular economy. By turning battery waste into valuable raw materials, these methods reduce the need for virgin material extraction and promote environmental conservation.
-
How do environmental regulations influence the battery recycling industry?
Environmental regulations play a crucial role in shaping the battery recycling industry by setting standards for waste management and resource recovery. Regulations often require manufacturers to implement end-of-life management programs for batteries, ensuring that they are recycled rather than discarded. This regulatory framework encourages companies to invest in recycling infrastructure and technology, driving innovation and efficiency. Moreover, compliance with these regulations helps companies avoid penalties and enhances their reputation for sustainability, which can be a competitive advantage in the market.
-
What role do industry players play in the advancement of battery recycling technologies?
Industry players are pivotal in advancing battery recycling technologies through investment, innovation, and strategic partnerships. Leading companies in the battery sector are developing closed-loop systems to recycle and reuse materials like lithium, nickel, and cobalt, thus reducing reliance on new raw materials. Collaborations between manufacturers and specialized recycling firms allow for resource pooling and technology sharing, enhancing the efficiency of recycling processes. These efforts not only meet regulatory requirements but also help secure a stable supply chain and reduce environmental impact.
-
How do safety concerns influence the development of new battery technologies?
Safety concerns are a major driving force behind the development of new battery technologies. Lithium iron phosphate (LFP) batteries, for instance, are gaining popularity due to their enhanced safety and lower cost compared to other chemistries. Emerging technologies like sodium-ion batteries are also being explored as they offer safer alternatives and reduce dependence on scarce materials. Addressing safety concerns not only protects consumers and the environment but also builds trust in new energy storage solutions, facilitating their broader adoption.
-
In what ways do strategic alliances enhance resource recovery in the battery industry?
Strategic alliances enhance resource recovery by enabling the sharing of expertise, infrastructure, and technology among different stakeholders, such as manufacturers, recyclers, and material suppliers. These partnerships allow for more efficient recycling processes, as companies can leverage each other's strengths to optimize material recovery. For example, a battery manufacturer might collaborate with a recycling firm to recover critical materials like lithium and cobalt without investing heavily in recycling facilities. These alliances also foster innovation, support a circular economy, and help companies meet environmental and regulatory standards more effectively.